
- #Traceroute gateway timeout 1 hop how to#
- #Traceroute gateway timeout 1 hop Pc#
- #Traceroute gateway timeout 1 hop series#
#Traceroute gateway timeout 1 hop Pc#
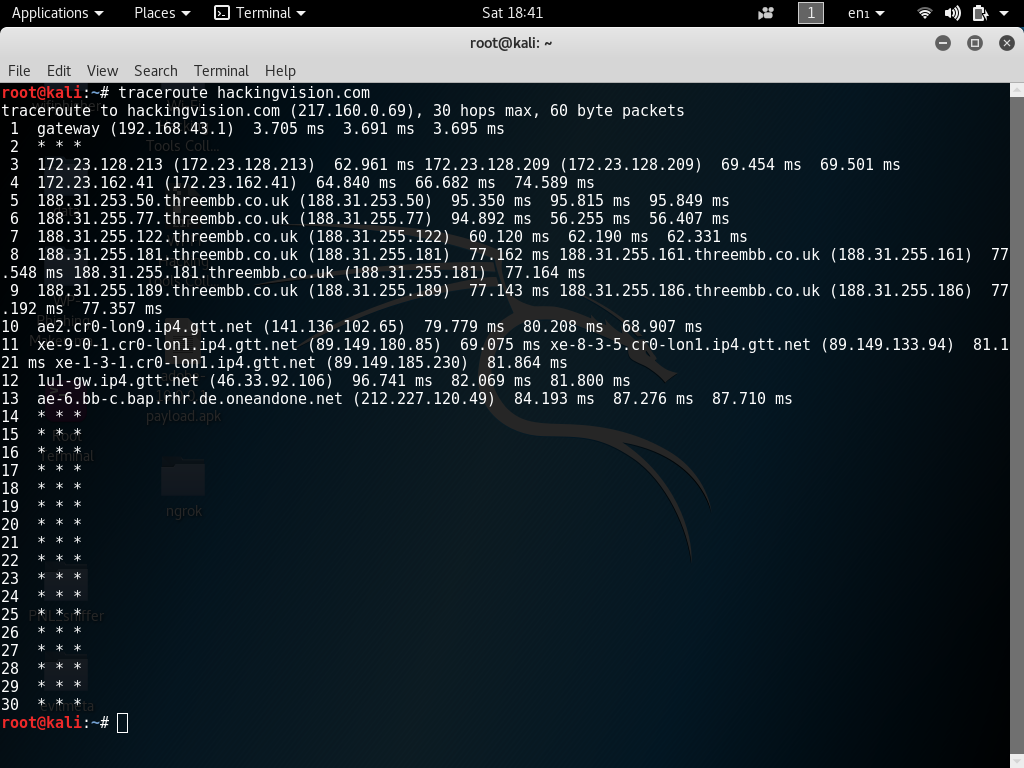
Usually, this is because they're used for hosting web pages or other security-sensitive services. I was actually 'tracert'ing from a PC to some outside host but the first hop returned was not my default gateway, but some other address (not even on my subnet). There are also some routers that disallow traceroute requests. A traceroute uses the asterisk symbol ( * ) to indicate such sensitive information. These nodes can only relay the packet but will not respond with any information about their network identity. It's possible that a node isn't sending any TIME_EXCEEDED packets back to the source. You can view how long each packet took to travel as well as any errors that were encountered. It'll also specify how long each leg of the journey took. Tracking the route ones packets fol- low (or finding the miscreant gateway thats discarding your packets) can be difficult. The output of the traceroute command will list every router in the path between your computer and the target host. This is a useful way to identify the general location of an issue within your ISP's network. The output lists every router that the packet goes through on its journey to The listed hops are ordered in terms of how close they are to your computer, the first hop being the closest.
#Traceroute gateway timeout 1 hop how to#
Now, you can figure out how to optimize your network setup to decrease response times in your application, service, or website by following the actual route between a server and your computer. This allows you to easily identify weak nodes that are affecting your network performance and the response time of each hop along the way You can also determine the round-trip delay between the probe host and each relay. Using a traceroute, you can identify each server along the route that receives your IP packet. Either way, you have a problem because your data is delayed and doesn't reach its destination within the expected time. Or maybe the packets were routed through an overloaded shared line. For example, there might be a problem at one of their servers or routers along the route. What if you had some sort of issue with your ISP's network? In that case, it could interfere with this process. It'd follow the same path to return the data. Finally, this packet reaches another ISP's router, which sends it to another router until it reaches its destination.
#Traceroute gateway timeout 1 hop series#
From there, it goes through a series of routers before arriving at an internet backbone router.This second router takes the packet to your ISP's regional network. From there, the router sends it to you through an intermediary router of your ISP's network.This communication starts by sending a packet from your computer to your local router.Imagine that you're trying to request some information from a faraway server


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
